Description
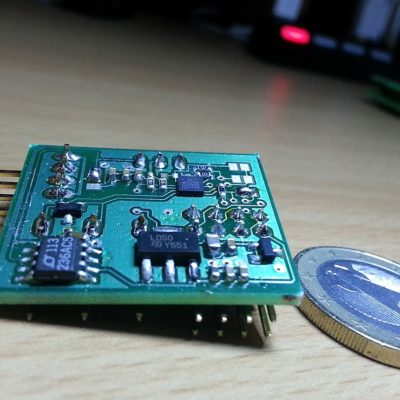
RS485 SnipCard for Archiduino system
This SnipCard enables communication in RS485 mode through the transceiver ST1480ACDR made by Texas Instruments. With breadbording cables you can easily adapt it to work with every Arduino board model.
The RS485 SnipCard is built on our highly reliable COM SnipCard. This SnipCard could be configured to work in many ways, like:
- CAN BUS interface;
- RS232 interface;
- RS485 interface;
- I2C buffered interface;
- 1WIRE buffered interface;
- I2C buffered, galvanically isolated interface;
- 1WIRE buffered, galvanically isolated interface;
- generic I/O buffer and / or galvanic isolation (in the range 0-10VDC);
- UART half duplex.
Techical specifications
The ST1480Ax is ±15 kV ESD protected, 3.3 V low power transceiver for RS-485 and RS-422communications. The device contains one driver and one receiver in half duplex configuration. The ST1480Ax transmits and receives at a guaranteed data rate of at least 12 Mbps. All transmitter outputs and receiver inputs are protected to ±15 kV using Human Body Model. Driver is short-circuit current limited and is protected against excessive power dissipation by thermal shutdown circuitry that places the driver outputs into a high-impedance state. The ST1480Ax input has a true fail-safe feature that guarantees a logic high output if both inputs are open circuit, shorted together or in the presence of a termination with no signal on the bus (from ST1480 datasheet).
Furthermore, the RS485 bus connector is secured by a single-line ESD-protection diode (according to IEC 61000-4-2: ± 30 kV contact discharge, ± 30 kV air discharge)
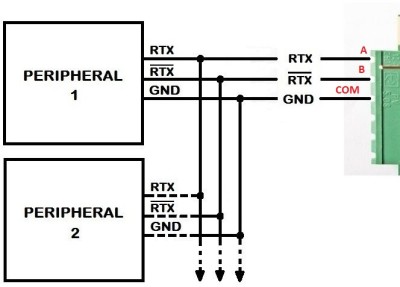
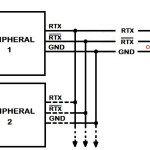
The bus 485 is a type of connection widely used in modules networks; it also allows you to make connections over long distances. Seletronica has created a I/O expansion device using the RS485 network and communicating with MBUS protocol.
TIA-485-A, also known as ANSI/TIA/EIA-485, TIA/EIA-485, EIA-485 or RS-485, is a standard defining the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in balanced digital multipoint systems. The standard is published by the Telecommunications Industry Association/Electronic Industries Alliance (TIA/EIA). Digital communications networks implementing the EIA-485 standard can be used effectively over long distances and in electrically noisy environments. Multiple receivers may be connected to such a network in a linear, multi-drop configuration. These characteristics make such networks useful in industrial environments and similar applications.
The EIA once labeled all its standards with the prefix “RS” (Recommended Standard), but the EIA-TIA officially replaced “RS” with “EIA/TIA” to help identify the origin of its standards. The EIA has officially disbanded and the standard is now maintained by the TIA. The RS-485 standard is superseded by TIA-485, but often engineers and applications guides continue to use the RS designation.
RS485 SnipCard description and examplesRS-485 enables the configuration of inexpensive local networks and multidrop communications links. It offers data transmission speeds of 35 Mbit/s up to 10 m and 100 kbit/s at 1200 m. Since it uses a differentialbalanced line over twisted pair (like RS-422), it can span relatively large distances up to 1,200 m (4,000 ft). A rule of thumb is that the speed in bit/s multiplied by the length in meters should not exceed 108. Thus a 50 meter cable should not signal faster than 2 Mbit/s.
(from Wikipedia)