Description
The RS-485 Serial Communication SnipCard allows to communicate in balanced digital multipoint systems with RS-485 standard. Iit can be used effectively over long distances and in electrically noisy environments. Multiple receivers may be connected to such a network in a linear, multi-drop configuration. These characteristics make such networks useful in industrial environments and similar applications.
RS-485 enables the configuration of inexpensive local networks and multidrop communications links. It offers data transmission speeds of 35 Mbit/s up to 10 m and 100 kbit/s at 1200 m. Since it uses a differential balanced line over twisted pair (like RS-422), it can span relatively large distances (up to 4,000 feet / 1,200 m). A rule of thumb is that the speed in bit/s multiplied by the length in meters should not exceed 108. Thus a 50 meter cable should not signal faster than 2 Mbit/s.
In contrast to RS-422, which has a single driver circuit which cannot be switched off, RS-485 drivers need to be put in transmit mode explicitly by asserting a signal to the driver. This allows RS-485 to implement linear bus topologies using only two wires. The equipment located along a set of RS-485 wires are interchangeably called nodes, stations or devices. (source: Wikipedia)
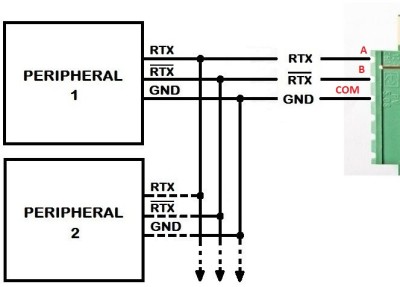
Motherboard connections
Technical specifications
- PIN A: TX+
- PIN B: TX-
- PIN COM: GND
Code example
/* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
ARCHIDUINO RS485 DEMO
The RS485 module (SM_UPC_COM RS485 version) must be connected
on socket #2 in order to meet the TX+ and TX- pins of the CPU
Motherboard Pinout:
- Pin A: RS485 TX+
- Pin B: RS485 TX-
- COM : RS485 GND
-------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* Includes ARCHIDUINO libraries */
#include <Archiduino.h>
#include <ArchiduinoLcd.h>
#include <pins_archiduino.h>
/* Includes ARDUINO libraries */
#include <LiquidCrystal.h> // required for Archiduino LCD libraries
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h> // required for Archiduino LCD libraries
#include <Wire.h> // required for Archiduino LCD libraries
#include <Serial.h>
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------
ArchiduinoLcd_PCF lcd; // set the LCD address to 0x20 for a 16 chars and 2 line display
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup() {
delay(1000);
lcd.init(); // initialize the lcd
lcd.begin(16, 2); // initialize lcd and keyboard
lcd.clear();
Serial1.begin(9600); // initialize the serial port 1
// Print a message to the LCD.
lcd.backlight(); // turn on the LCD backlight
lcd.print(" ARCHIDUINO ");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" DEMO RS485 ");
}
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop()
{
Serial1.println("THIS IS A RS485 TEST");
delay(500);
}